Feb-21 CPI Inflation: Quick rebound from the lows
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- CPI inflation accelerated sharply to 5.03% YoY in Feb-21 from 4.06% in Jan-21.
- The up move was broad-based with all three key sub-categories of food, fuel, and core inflation carrying higher inflation prints.
- Barring seasonal influences, food inflation could moderate in FY22 if it is supported by a favorable monsoon outturn.
- However, there is upside risk to both fuel and core inflation as global commodity prices have risen sharply and producers could pass on higher raw material prices amidst an anticipated V-shaped recovery along with progress in vaccination in the backdrop.
- For FY22, we continue to expect average CPI inflation to moderate close to 5.0% from the estimated average of 6.2% in FY21.
- While this would be comforting, it would also mark the third successive year of overshooting of the mandated target (which we expect to be retained at 4.0% by the government in its upcoming review of the existing flexible inflation targeting framework in Mar-21).
After dropping to sub 5% levels briefly, CPI inflation accelerated sharply to 5.03% YoY in Feb-21 from 4.06% in Jan-21. On sequential basis, while the jump in CPI at 0.19% MoM in Feb-21 appears modest, its relatively much higher in comparison to a contraction of 0.73% MoM seen in Feb-20. This explains the exaggerated impact coming from the adverse base effect in Feb-21.
Drivers of inflation
- Annualized food inflation jumped to 4.25% in Feb-21 from recent low of 2.67% in Jan-21. At a granular level, Oils & Fats and Non-Alcoholic Beverages, with cumulative weight of 4.8% in the CPI basket, are two sub-categories currently facing record high levels of annualized inflation (20.8% YoY and 13.9% YoY respectively). Moving on to heavyweight and volatile items like Vegetables, we note that the seasonal sequential easing is running out with possibility of fresh buildup in prices during the month of Mar-21, aided by the early onset of summer and upward revision in transportation charges.
- Consolidated fuel inflation (fuel and light index along with fuel items within miscellaneous index) accelerated to a 2-year high of 6.94% YoY in Feb-21 from 5.67% in Jan-21. Continued ascent in consolidated fuel inflation in the last 3-quarters manifests the steep rise in price of international crude oil, with India Crude Basket moving from an average of USD 21 per barrel in Apr-20 to USD 55 per barrel in Jan-21. Expectation of a strong V-shaped recovery in global growth along with supply management by OPEC has led to further build-up of price pressures, with India Crude Basket climbing up further to USD 65 per barrel levels in the month of Mar-21 so far.
- Core inflation (headline ex. food and fuel items), reflecting underlying demand conditions in the economy, also hardened to a near 2-year high of 5.36% YoY in Feb-21 from 4.90% in Jan-21. This is somewhat of a concern and needs to be kept under watch as any Covid-19 related disruption in supply could result in inflationary pressures as the economy moves towards fast normalization in the backdrop of ongoing vaccination and increase in raw material prices.
Outlook
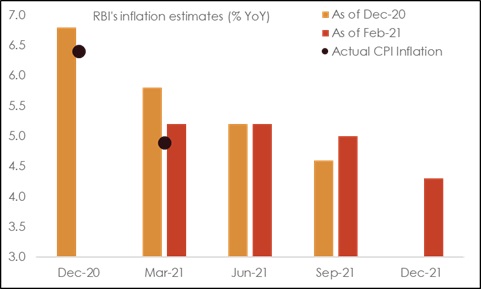
Despite the acceleration in price pressures, we note that CPI inflation is currently tracking at 4.9%, below RBI’s forecast of 5.2% for Q4 FY21. This indeed offers a mild solace. In addition, record rabi sowing also provides comfort as it is likely to keep food price pressures somewhat under check in the coming summer months.
Going forward beyond the near term, the south-west monsoon outturn, strength of demand recovery, pace of supply restoration, and trajectory of commodity prices would determine the overall inflation trajectory. Also, any government action on reduction of fuel taxes will require a careful balancing of fiscal consideration and inflation/sentiment impact.
Assuming a normal monsoon, strong V-shaped recovery in growth and range-bound commodity prices vis-à-vis current levels, we continue to expect headline inflation to moderate towards 5.0% levels on average basis in FY22 from an estimated level of 6.2% in FY21.
While this would be comforting, it would also mark the third successive year of overshooting of the mandated target (which we expect to be retained at 4.0% by the government in its upcoming review of the existing flexible inflation targeting framework in Mar-21).
Annexure
Table1: Key highlights of CPI inflation data
| Overview of CPI Inflation by components (% YoY) |
|
Feb-20 |
Jan-21 |
Feb-21 |
Apr-Feb FY20 |
Apr-Feb FY21 |
| CPI |
6.58 |
4.06 |
5.3 |
4.66 |
6.24 |
| Food & Beverages |
9.45 |
2.67 |
4.25 |
5.89 |
7.56 |
| Pan, Tobacco & Intoxicants |
4.10 |
10.87 |
10.70 |
4.11 |
9.92 |
| Clothing & Footwear |
2.05 |
3.82 |
4.21 |
1.57 |
3.28 |
| Housing |
4.24 |
3.25 |
3.23 |
4.61 |
3.32 |
| Fuel & Light |
6.36 |
3.87 |
3.53 |
0.90 |
2.52 |
| Miscellaneous |
4.51 |
6.49 |
6.82 |
4.43 |
6.52 |
| Memo Items |
| Consolidated Fuel |
5.63 |
5.67 |
6.94 |
-0.01 |
4.51 |
| Core-Core |
3.42 |
4.90 |
5.36 |
3.92 |
4.77 |
Note: For FY21, Apr-Jun data for Consolidated Fuel and Core-Core inflation is not available
Despite fast acceleration, inflation in Q4 FY21 is tracking below RBI’s estimates