
The Indian paper industry contributes 3.7% to the global production of paper. The global paper and paperboard market was estimated at ~415 million tonnes (MT) in 2018 and is expected to grow to 470 MT by 2030 owing to rising demand. As per Indian Paper Manufacturers Association (IPMA), the annual turnover of the Indian paper industry is estimated at ~Rs. 60,000 crore. India’s per capita paper consumption currently stands at ~13 kg way below the global average of 57 kg. In fact, the consumption is even below the Asian average of 40 kg signifying positive growth momentum going ahead. The paper industry is broadly classified into four segments - Packaging Paper/Board which contributes ~50%, Writing & Printing (W&P) (~30%), Newsprint (~16%) and Specialty Papers & Others (~4%) to the total industry.
In FY19, overall demand of paper in India grew at 6.4% y-o-y to 18.6 million tonnes (MT) from 17.5 MT in the previous year. Segment wise packaging paper/board grew at a healthy 8.5% y-o-y to 9.7 MT whereas W&P segment grew ~4% y-o-y to ~5 MT. At a broad level, paper consumption in India is rising at a healthy rate on account of rising income levels, increasing literacy rates, improvement in the standard of living and out-of-home consumption.
The market size of W&P segment stood at 5.4 MT in FY19 witnessing a growth of ~4% y-o-y. The segment primarily includes uncoated paper (~85%) and coated paper (~15%). Rising literacy rate, universalization of education through government measures like Right to Education, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan and mid-day meal scheme coupled with increase in educational spending are likely to be the major growth drivers for the segment going ahead.
Raw materials used in production of paper include wood, bamboo, recycled fibre, bagasse, wheat straw, rice husk, etc. In terms of share in overall paper production, ~25% is based on wood/bamboo, ~58% on waste paper/recycled fibre and ~17% on agro-residues (bagasse/wheat straw). Going ahead, access to good quality and cost competitive raw materials to remain a key monitorable for the industry.
Key Risks & Attributes

The W&P paper segment market size in India grew by ~4% y-o-y to 5.4 MT in FY19. The steady growth was supported by increase in literacy rates and universalization of education through steps taken by the government. However, despite witnessing the steady growth, the per capita paper consumption of the country stands at a subdued 13 kg which is lower compared to the global average of ~57 kg. The industry partially remains susceptible to ongoing digital technologies thereby posing threat to the consumption of W&P paper segment in near future.
However, pick-up in the education sector and growing enrolment as well as increasing number of schools, colleges and institutions along with spending on education is expected to increase demand for W&P papers.
Acuité believes that owing to the rising literacy rates and growth in education sector rurally, will continue to create stable demand going ahead.

The Indian paper industry is highly fragmented with 750 to 800 paper mills situated across the country. However, the competitiveness is influenced by the type of raw materials being used for manufacturing of paper. For instance, wood pulp-based mills possess high entry barriers owing to scarcity of the raw material, high power & water consumption and location issues on account of the requisite environmental clearances. Further, being capital intensive business players continuously optimize their cost structure’s allowing them to mitigate competition in the domestic market.
On the other hand, waste paper and agro-based mills witness low entry barriers owing to it being relatively less capital intensive. Consequently, there is high level of competition within players which cripples their margins as well. Notwithstanding, at a broad level, organized players continue to be differentiated with better access to raw materials and high level of investments in technology which helps them produce superior products.
Moreover, the domestic industry also faces immense competition of imports from ASEAN countries which are of superior quality and of lower prices. Imports are further supported by progressive reduction in the basic customs duty by India on paper imports under the FTAs signed with ASEAN and South Korea. With the domestic paper manufacturers being less competitive against imports, given their superior quality coupled with lower prices, the industry is likely to continue to face competition going ahead as well.
Acuité believes that the industry remains exposed to moderate competitive intensity and will remain a key monitorable going ahead.

Manufacturing units of W&P paper industry majorly depend on wood pulp which is the major raw material used for manufacturing the requisite paper. As per IPMA, in FY19 the demand for pulpable wood by the industry was ~11 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) while domestic availability is ~9 MTPA. In fact, inadequate availability of the same in the country has been a major constraint for the industry due to which the domestic players depend on imports for meeting their raw material needs. Consequently, players are vulnerable to price volatility & foreign exchange risks which impacts their profitability.
Thus, with the W&P paper industry’s higher reliance on wood pulp based raw materials, any inadequate availability of the same increases input-related risks.
Acuité believes that the input related risk to the sector persists due to inadequate availability of wood pulp domestically exposing the industry to imports.

The W&P paper industry is subject to stringent environmental and pollution control norms as paper mills contribute significantly to air and water pollution. Players in the industry have to comply with stringent effluent treatment norms of pollution control boards and depend on complete discretion of the government which leads to high compliance risks. However, most of the pulp-based paper mills have adopted environment friendly technologies to minimize wastage and maximize recycling/reuse materials to produce eco-friendly paper.
The industry is also vulnerable to dumping risk with any reduction in the basic customs duty by India on paper imports under the FTAs signed with ASEAN and South Korea. With the domestic paper manufacturers being less competitive against imports, given their superior quality coupled with lower prices, the industry remains susceptible for the same.
Acuité believes that regulatory risk persists in the paper industry due to requirement of continuous adherence to environmental regulations. In fact, investments are required to comply with these norms which can impact players’ profitability.

Organized players have already increased investments on research and development (R&D) for technological upgradation to ensure better compliance and optimum utilization of key resources.
However, smaller paper manufacturers are more prone to using obsolete technology where raw material and power consumption is higher as compared to modern paper mills. Adoption of new technology by these players would lead to cost reduction, optimal consumption of raw material coupled with compliance to several regulatory norms. Notwithstanding, this requires investments by players which can impact their profitability leading them to avoid this transition.
Increasing digitization and latest technological gadgets offering higher storage capacity and portability poses a substitution threat to the industry.
Acuité believes that organized players have or are transitioning to newer technologies thereby alleviating risk.
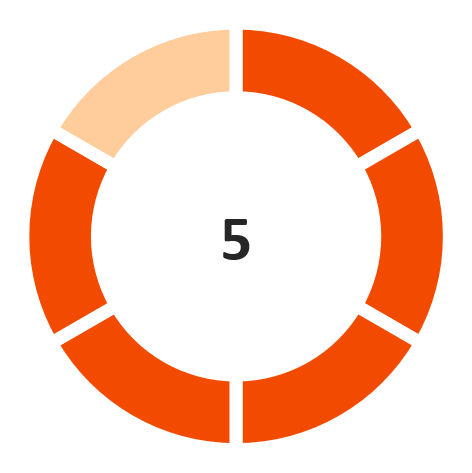

Operating Margin
(Favorable)
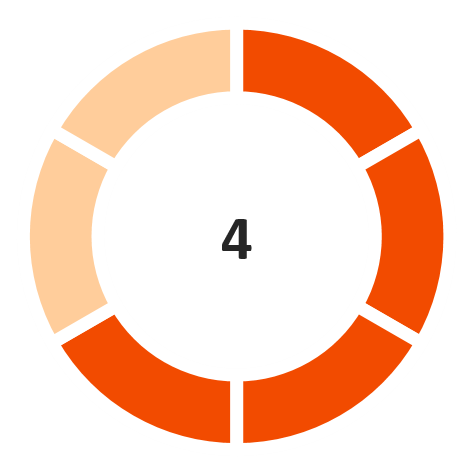

Interest Coverage Ratio
(Marginally favorable)
Return on capital employed
(Marginally unfavorable)

Debt/ Equity
(Marginally favorable)

GCA days
(Marginally unfavorable)
Note: The industry financial performance risk score is provided on a 6-point scale
Disclaimer:
Acuité IRS should not be treated as a recommendation or opinion that is intended to substitute for a financial adviser's or investor's independent assessment of whether to buy, sell or hold any security of any entity forming part of the industry.
Acuité IRS is based on the publicly available data and information and obtained from sources we consider reliable. Although reasonable care has been taken to ensure that the data and information is true,
Acuité, in particular, makes no representation or warranty, expressed or implied with respect to the adequacy, accuracy or completeness of the information relied upon.
Acuité is not responsible for any errors or omissions and especially states that it has no financial liability whatsoever for any direct, indirect or consequential loss of any kind arising from the use of Acuité IRS.