Executive Summary
India has a large number of government entities and industrial growth to a great extent is attributed to these entities formed either by an act of parliament or by orders of the central/state cabinets. Such entities play a central role in the economic growth of the country.
These organisations, spread across sectors from Civil Supplies to State Road Transportation are the catalysts of socio-economic prosperity. They are systemically essential and their perpetual existence enables the government to diligently discharge its key roles and responsibilities. To this end, their smooth functioning and subsistence is a significant policy interest of the respective state and central governments and, Acuité believes that a certain degree of support is generally extended towards such entities by state governments. Such support can be in any form - from unconditional guarantees to significant shareholding to letter of comfort. However, the impact of such support varies from case to case and thus, Acuité assigns a state government notch up to government entities - which is a function of the credit risk and ability of the state government to support the entity being rated.
Objective
The objective of this document is to describe the methodology used to assign government notch up to eligible public sector undertakings and other government entities in India.
Methodology to Identify the Nature and Degree of Government Support:
Acuité follows a three tier process to understand the nature, degree and likelihood of government support extended/to be extended towards various entities:
The significance of the entity is also evaluated on the basis of the strategic role and importance of the sector in the state/central government's policy. Schematically, the relationship may be summarised as follows:
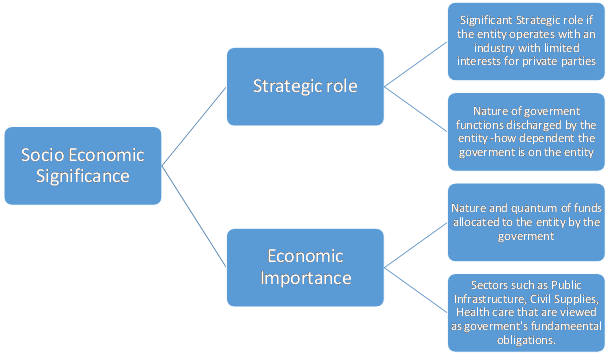
Acuité believes that the degree of support extended by the government to any related entity is a function of two key parameters:
Determining the Degree of Government Notch Up
Acuité may follow a three dimensional approach to determine the degree of government notch up to be extended to any entity, as discussed below:
|
Parameters |
Significant Shareholding by the Government |
Implications of Default |
||
|
High |
Low |
|||
|
Socio Economic Significance |
High |
Yes |
Such entities are extremely important for the smooth functioning of the government, and thus, Acuitéequates the rating of such entities with the respective government ratings. |
Such entities are expected to remain solvent through periodic support from the government. However, low implications of the entity defaulting is also adequately factored in the notch up. |
|
No |
While such entities are systemically essential, the absence of significant shareholding induces some uncertainty with respect to the degree and nature of support expected from the government. |
Low implications of default further dilutes the degree of support as a result of which, limited government support is assumed in such cases. The notch up in such cases is limited. |
||
|
Moderate |
Yes |
Such entities, like certain financial institutions are expected to receive significant support from the government due to the goodwill they enjoy. |
Only support such entities are expected to receive from the government is due to the role they play in discharging public policy objectives across the policy spectrum. |
|
|
No |
The notch up in such cases is relatively lower as compared to the case discussed above due to the absence of significant government holding making it a largely private enterprise with limited government holding -ineligible for large budgetary allocations. |
Low implications of default further dilute the degree of support. As a result, limited government support is assumed in such cases. |
||
|
Low |
Yes |
The singular motivation for any support is driven by the adverse implication of default, thus limited support is expected and resulting in minimal benefit to the credit profile of the rated entity. |
Despite high government holding, the relatively limited economic and political significance of the entity reduces the probability of government support in case of distress. |
|
|
No |
While the entity is important for the government, there's limited statutory provision available to extend support. Thus, minimal notch up is extended by Acuité. |
No notch up. |
||